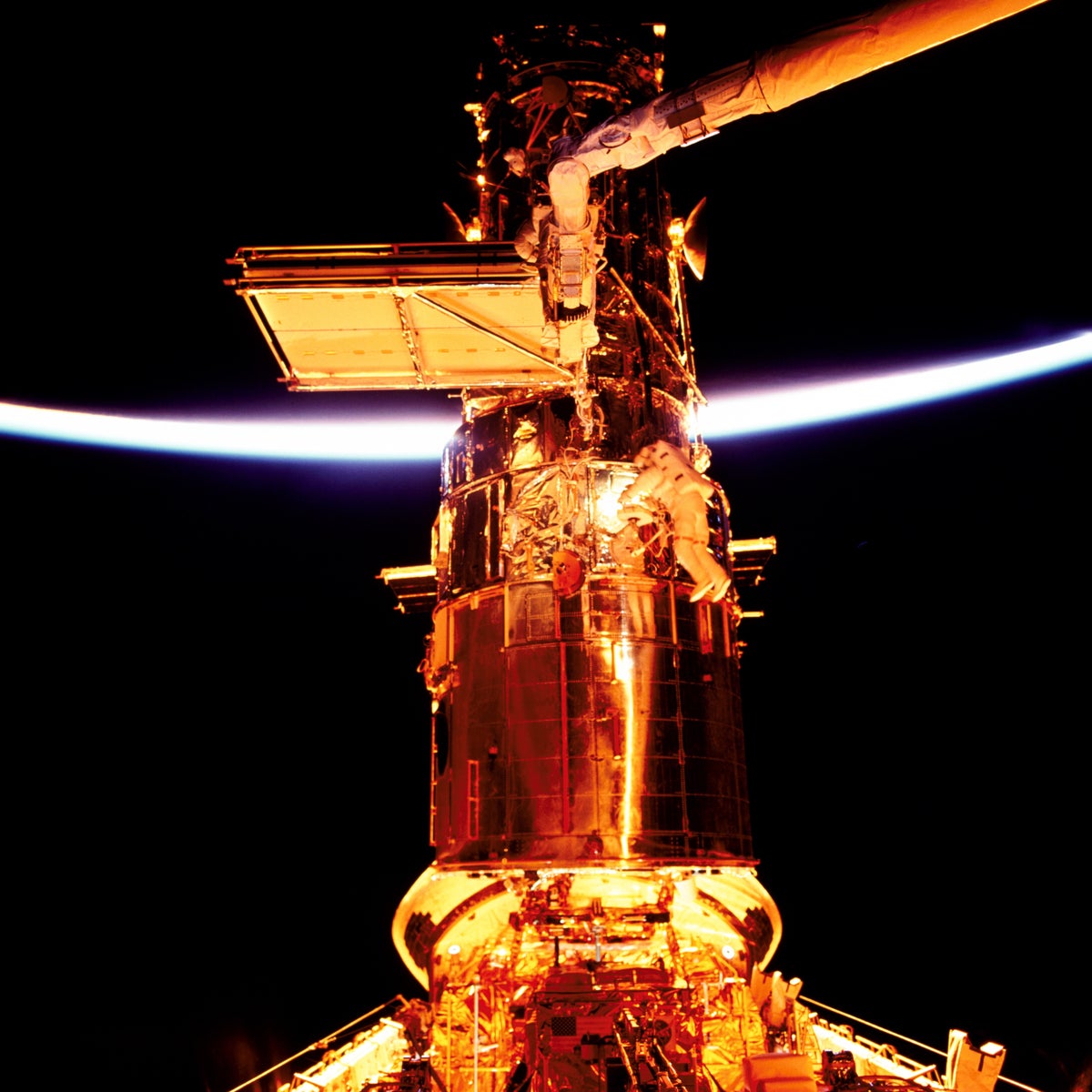
"On April 24, 1990, humanity launched a scientific revolution. I mean launched literally: on that date the space shuttle Discovery roared into the sky with the Hubble Space Telescope nestled in its cargo bay. The telescope was on a mission destined to forever change our view of the universe. Hubble wasn't the largest telescope everits 2.4-meter mirror is actually considered small these daysbut being above the atmosphere gave it superpowers."
"Our air boils and roils, blurring the views from ground-based instruments. It glows, toodimly but enough to limit how faint an object astronomers can see. And third, our air absorbs most ultraviolet and infrared light, where interesting things happen, cosmically speaking. Getting up, up and away from all that atmosphere made Hubble one of the most important telescopes ever built."
"Hubble saw objects fainter than had ever been observed before. The telescope homed in on how fast the universe expands, watched weather changes on the outer planets and proved that every big galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its heart, just to name three amazing feats off the top of my head. The major breakthroughs and discoveries that came out of this magnificent machine are so numerous, really, that even listing them here would be excessive."
The Hubble Space Telescope launched on April 24, 1990 aboard the space shuttle Discovery. Hubble's 2.4-meter mirror is modest by modern standards, but its position above Earth's atmosphere provided decisive advantages. Earth's atmosphere blurs astronomical images through turbulence, adds sky glow that limits faint-source detection, and absorbs most ultraviolet and infrared light. Operating above the atmosphere enabled Hubble to observe much fainter objects, access ultraviolet wavelengths, and deliver sharper images than ground-based telescopes. Hubble produced major results including measurements of the universe's expansion rate, observations of outer-planet weather, and confirmation that large galaxies host central supermassive black holes. NASA's James Webb Space Telescope was not intended to supplant Hubble, and calling JWST Hubble's replacement is inaccurate.
#hubble-space-telescope #space-telescopes #atmospheric-effects #astronomical-discoveries #james-webb-space-telescope
Read at www.scientificamerican.com
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]